Understanding your roof’s pitch is one of the most important first steps in any roofing project. It might sound like technical jargon, but this simple measurement is a critical factor that influences everything from material choices and project cost to your home’s ability to handle Texas weather. This guide is designed to demystify the process, providing clear explanations and a simple tool to help you understand what you’re working with.
Roof Pitch Calculator
Enter the rise and run measurements of your roof to calculate the pitch and angle.
Roof Pitch:
Roof Angle:
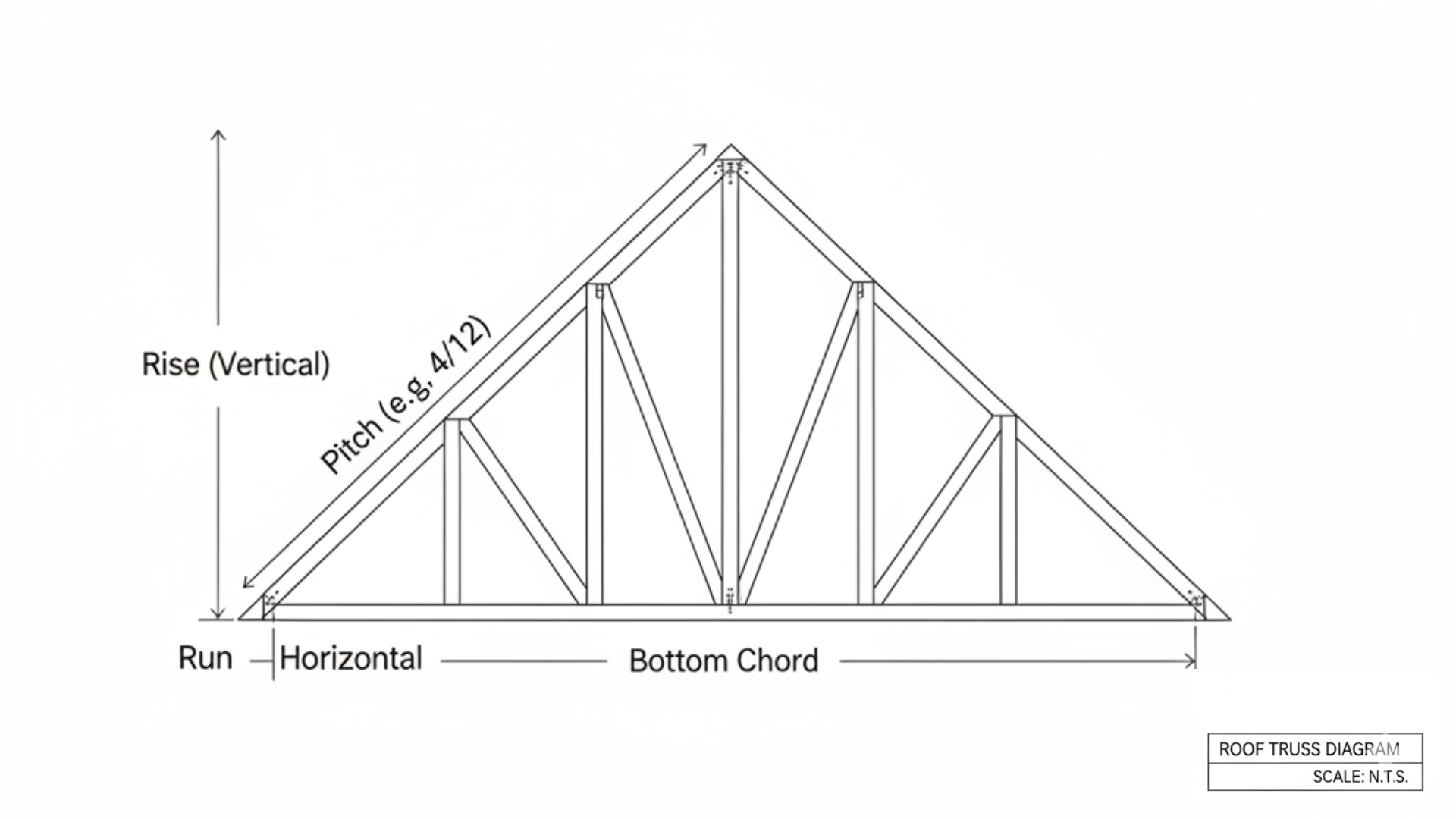
Understanding the Language: What is Roof Pitch?
Roof pitch is a measurement of a roof’s steepness. It’s expressed as a ratio of “rise over run,” where:
- Rise: The vertical height of the roof.
- Run: The horizontal distance of the roof.
The ratio is always presented as inches of rise for every 12 inches of run. For example, a “6/12 pitch” means the roof rises 6 inches vertically for every 12 inches it extends horizontally.
Two Simple Methods for Measuring Your Roof’s Pitch
While our calculator does the math, you still need to get the initial measurements. Here are two common, practical methods.
Method 1: The Rafter / Attic Method
This is the safest and often most accurate method.
- From inside your attic, place a level horizontally against a rafter or the underside of the roof deck.
- Measure 12 inches along the level—this is your “run.”
- From that 12-inch mark, measure vertically up to the underside of the roof deck. This measurement is your “rise.”
- If you measured a rise of 8 inches, you have an 8/12 pitch.
Method 2: The Level Method (From the Roof Surface)
If you cannot access the attic, this method works from the outside.
- Place a 12-inch (or 24-inch) level flat against the surface of your shingles.
- Raise the downhill end of the level until the bubble is perfectly centered.
- Measure the vertical distance from the roof surface to the bottom of the raised end of the level. This is your “rise” for that length.
- If you used a 12-inch level, that measurement is your rise. If you used a 24-inch level, divide the measurement by 2.
Why Your Roof’s Pitch is a Critical Factor
- Material Compatibility: Many roofing materials, especially certain types of shingles, have minimum pitch requirements to shed water effectively.
- Water & Debris Shedding: A steeper pitch allows rain, leaves, and other debris to run off more efficiently.
- Project Cost & Complexity: Steep-slope roofs are more difficult and dangerous to work on, which increases the overall cost of the project.